Sustainability
Water risk assessment
Water is an important resource for our group's business activities and local communities. We understand the amount of water resources used at each production site in Japan and overseas, the quality of water at the time of drainage, etc., and not only devise ways to use it internally and manage wastewater appropriately, but also contribute to the supply chain by using our products. In addition to working to reduce our environmental impact, we also conduct risk assessments to ensure sustainable business growth.
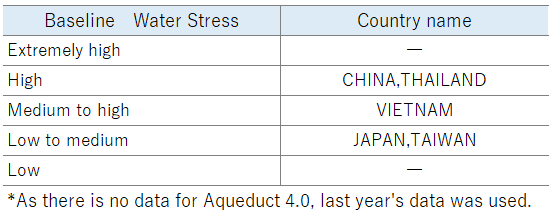
Water stress situation in countries where our group's production bases are located
Evaluation of the Aqueduct Country Ranking developed by the World Resources Institute as a tool for commonly assessing water risks in specific countries.
We use the index Baseline Water Stress (adopting the BAU scenario to predict the amount of available water resources in 2030) to check the water stress situation in the countries where our group's production bases are located.
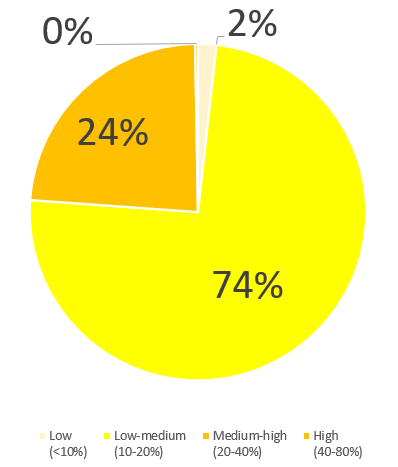
Regarding the water stress situation in the basin where our group's production and research bases are located
In addition to assessing the water stress of the countries where our production sites are located, we also assess the latitude and longitude of our domestic and overseas production sites and research laboratories, and conduct risk assessments based on the water stress situation in the river basins where they are located, the water usage and water quality of each site, and the status of the products produced. When we re-evaluated in August 2024, we found that our site in Thailand was in an area with a relatively high water resource risk, but it was not a site with a high water usage volume, accounting for approximately 0.3% of the total, and the areas with medium to high risk accounted for approximately 24% of the total. We also conduct risk assessments for each of our business sites in Japan and overseas every year, and we recognize water risk as one of the various risks, but we have not set any reduction targets within our group. More than that, we view the use of our products as an opportunity to reduce wastewater loads through the supply chain, and we are working on our business activities.
.
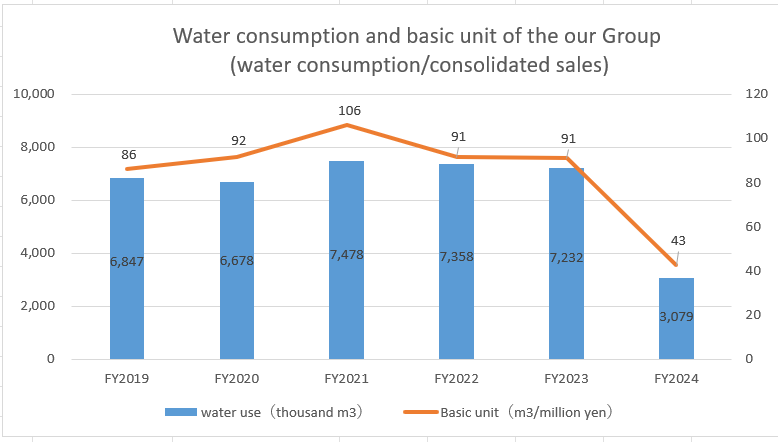
Trends in water resource usage/drainage volume, etc.
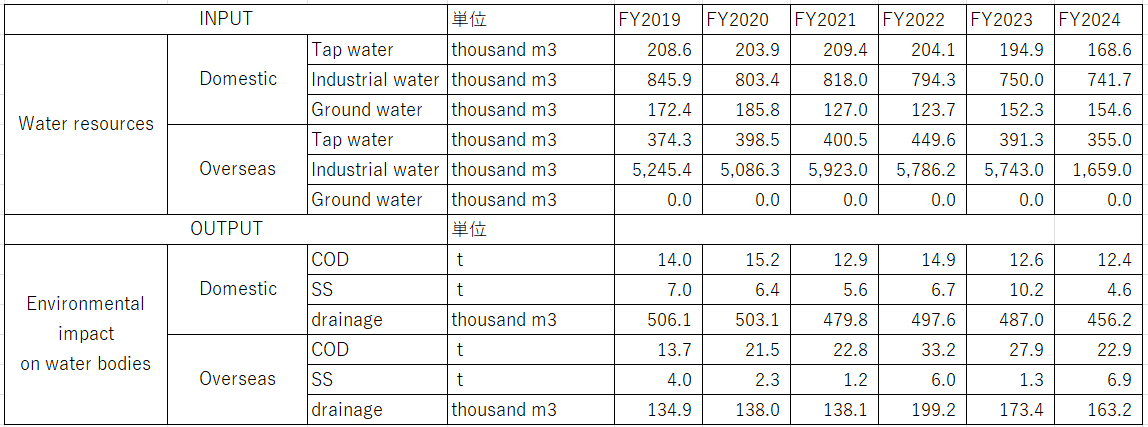
Arakawa Europe's results for fiscal year 2023 are based on results up until early April 2023, when production activities were taking place, so water usage has decreased.
water resources graph
Conservation of water resources
Sewage generated during the manufacturing process (washing water, etc.) is purified at a wastewater treatment facility. We set and monitor voluntary targets for chemical oxygen demand (COD) and suspended solids (SS), and discharge the waste outside the factory after confirming that it is well below regulatory values.
✓ Initiatives to reduce factory wastewater generation
Our group requires water not only for manufacturing products, but also for cleaning equipment, which uses a lot of water and energy, and generates a large amount of wastewater. After thoroughly confirming safety and product quality and reviewing the cleaning method, we were able to significantly reduce annual water consumption by approximately 1,000 tons and annual electricity consumption for equipment operation by approximately 6,000 kWh. It also reduced the number of times the machine needed to be washed, which led to improvements in productivity such as a reduction in operator workload.Additionally, at our Vietnam site, we have begun reusing water used to rinse pots in order to reduce the amount of wastewater discharged from our manufacturing facilities.
✓ Improving the efficiency of wastewater treatment through system management
In wastewater treatment, wastewater generated at each manufacturing plant is collected and treated, but the conditions of the collected wastewater change, so it is always difficult to deal with it.
In particular, we have continued to make improvements because, depending on the quality of the treated water, it may not be possible to release the water, leading to the suspension of production at the factory. We have introduced the S.SensingCS system, which automatically increases or decreases the amount of flocculant (sulfuric acid band) injected according to the quality of the wastewater. Before the system was introduced, a five-month test period was established to determine its ability to respond to changes in water quality and its effectiveness. As a result, the wastewater treatment conditions were stabilized, and the amount of flocculant was reduced compared to the conventional method, resulting in a reduction in the amount of sludge generated (△10%).
In the future, we will continue to promote stable and efficient wastewater treatment and waste reduction in an effort to reduce our environmental impact.
Reducing wastewater load in the supply chain
Our group operates paper manufacturing chemicals business not only in Japan but also overseas, and we use a lot of water when manufacturing our products. Corrugated cardboard is a recyclable packaging material, but repeated recycling causes a decrease in the strength of the pulp fibers themselves, so paper strength agents are widely used as chemicals to strengthen the strength of corrugated paperboard. In response to the needs of the times, we have continuously developed technology and supported waste paper recycling in Japan. In some regions overseas, such as Southeast Asia, starch, which has a large wastewater load, is still used in the production of corrugated paperboard. Our products can achieve a high yield effect with a small amount of addition, and can reduce wastewater load. We will expand the business model that supports Japan's waste paper recycling overseas and contribute to its widespread use.
Recently, we have been developing products that not only reduce CO2 emissions but also reduce water consumption by increasing product concentration while maintaining the same performance as conventional products, and we are working on further improvements throughout the supply chain.